Clinical Immunology focuses on the immune system’s health. Learn about the diagnosis and treatment of allergies, autoimmune diseases, and immunodeficiencies.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.

Diagnosing Sjögren syndrome can be challenging because dryness is a common symptom in many people. To confirm the disease, doctors need to do specific tests to show it is caused by autoimmunity. At Liv Hospital, we use guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism. Diagnosis involves blood tests, eye exams, tests of gland function, and sometimes looking at tissue under a microscope.
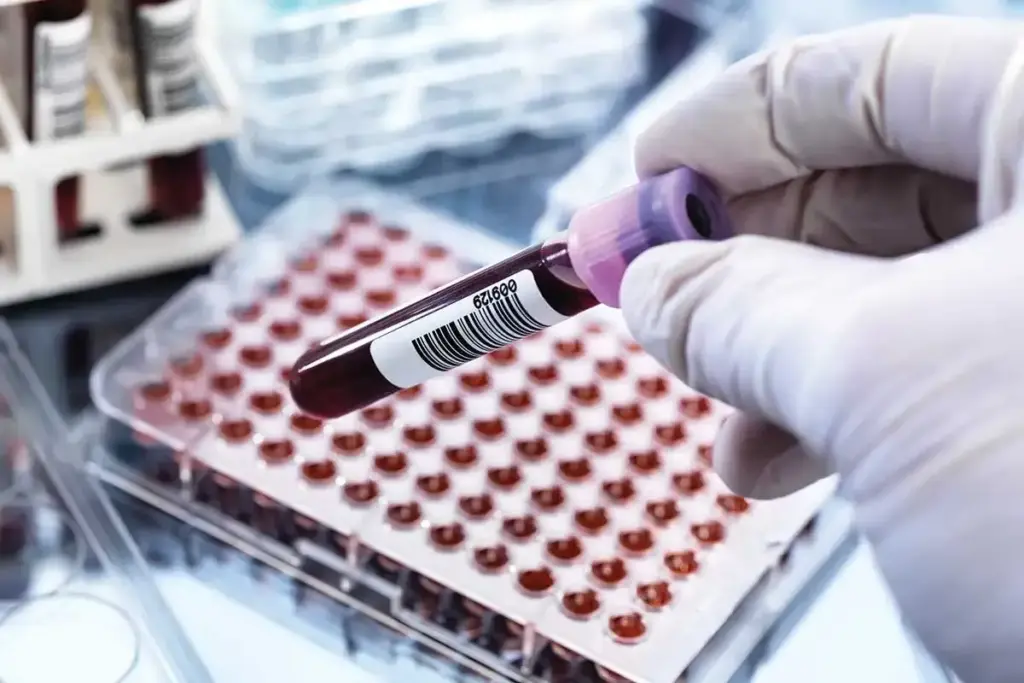
Blood tests are the first step. The presence of anti-SSA (Ro) antibodies is the most heavily weighted criterion for diagnosis.
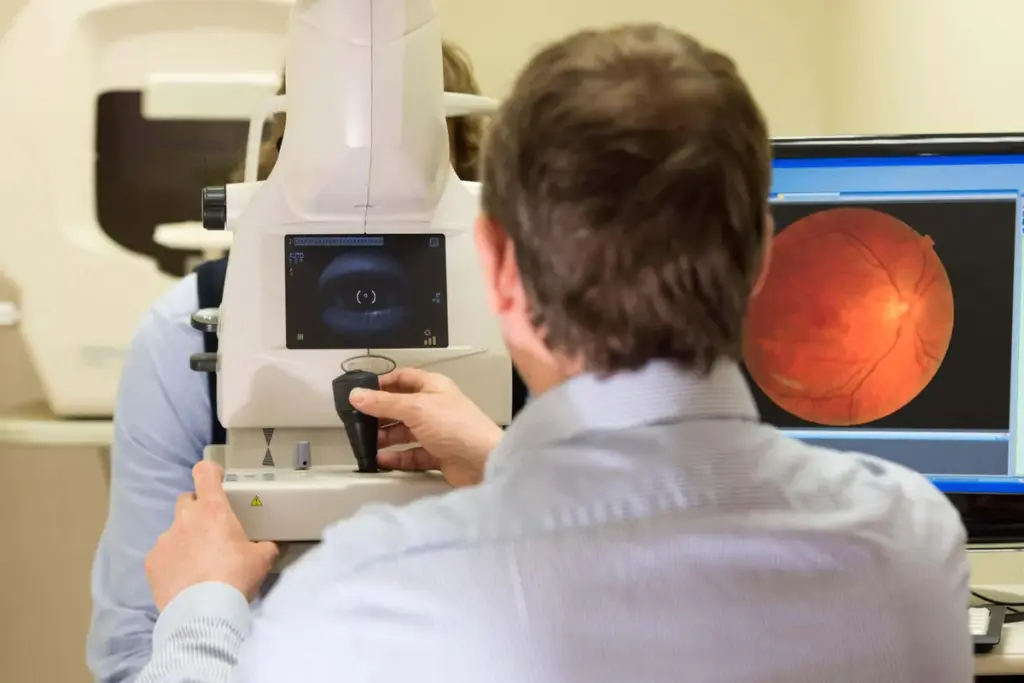
Ophthalmologists use specific tests to objectify dry eye symptoms.
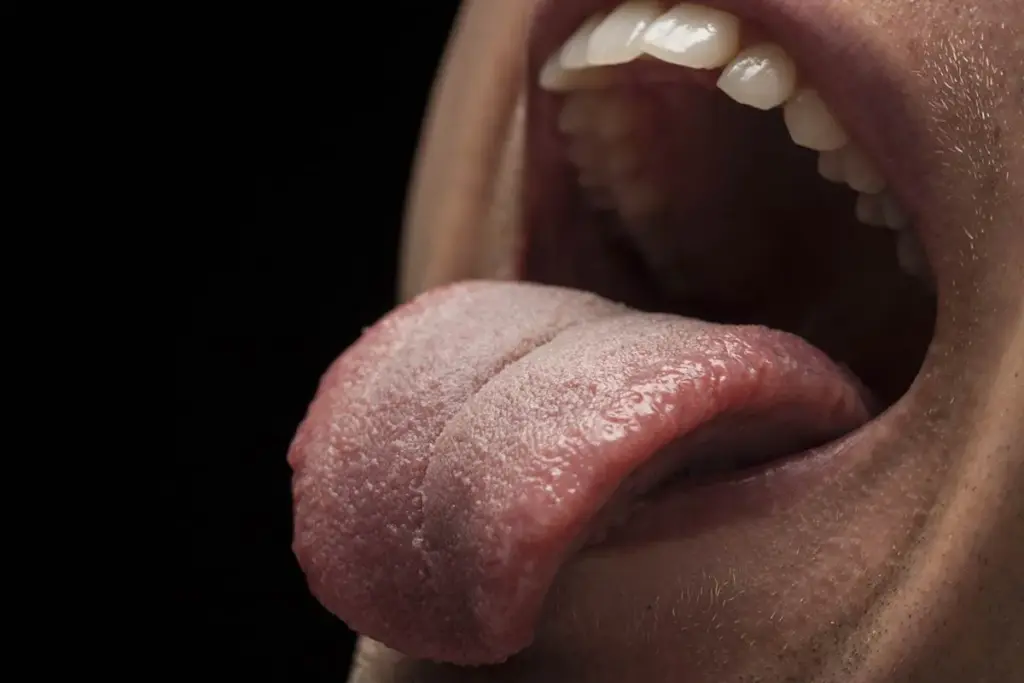


When serology is negative or the diagnosis is unclear, a lip biopsy is performed.
The diagnosis is a diagnosis of exclusion. Many conditions mimic Sjögren syndrome.
Research is ongoing to identify new non-invasive markers.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
It allows doctors to see the actual immune attack in the tissue. For patients who test negative for antibodies in the blood, the biopsy is the only way to prove the disease exists.
It can be slightly irritating as the paper touches the eye, but it is not painful and is over in five minutes.
A positive ANA suggests an autoimmune process, but it is not specific to Sjögren’s. It must be interpreted alongside Anti-SSA/SSB tests and clinical symptoms.
MRI is excellent for evaluating glandular structure and ruling out tumors, but it is typically reserved for complex cases or when lymphoma is suspected.
Unfortunately, the average time to diagnosis is several years because symptoms are often dismissed. Seeing a rheumatologist early is key to speeding up this process.


Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)